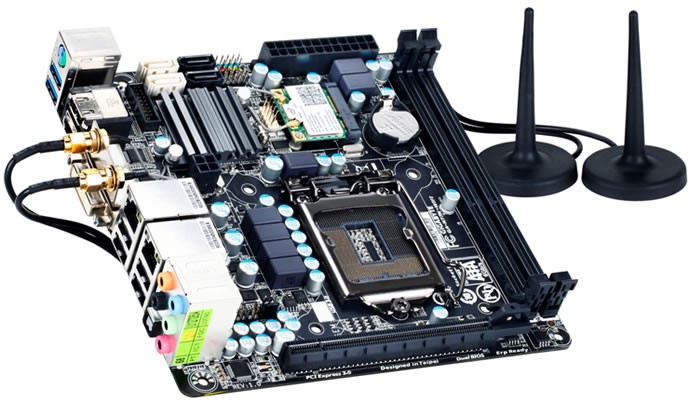
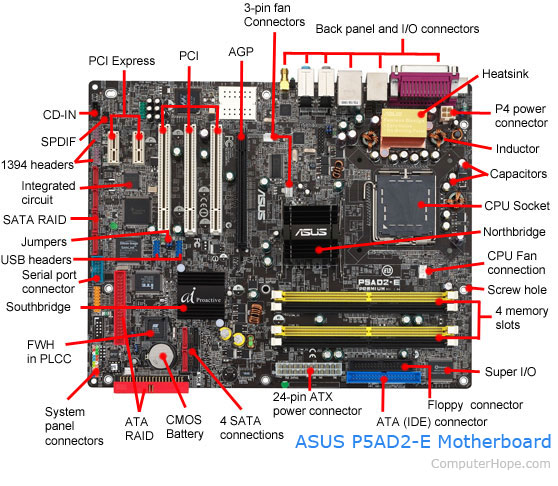
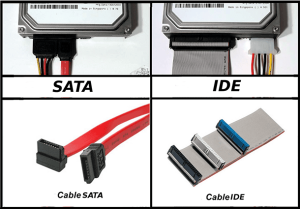
Motherboard: Definition
A motherboard is one of the most essential parts of a computer system. It holds together many of the crucial components of a computer, including the central processing unit (CPU), memory and connectors for input and output devices. The base of a motherboard consists of a very firm sheet of non-conductive material, typically some sort of rigid plastic. Thin layers of copper or aluminum foil, referred to as traces, are printed onto this sheet. These traces are very narrow and form the circuits between the various components. In addition to circuits, a motherboard contains a number of sockets and slots to connect the other components.
Motherboard is also called the heart of a computer. Because it consists of electronic path ways (called the Data Buses) on the back side that connect all the devices to CPU socket like a heart.
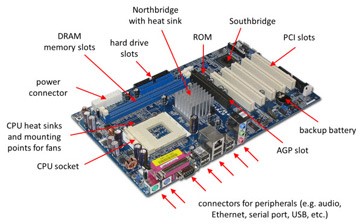
Parts of a Motherboard
If you were to open up your computer and take out the motherboard, you would probably get pretty confused about all the different parts. Depending on the make and model of your computer, it might look something like this.
To understand how computers work, you don’t need to know every single part of the motherboard. However, it is good to know some of the more important parts and how the motherboard connects the various parts of a computer system together. Here are some of the typical parts:
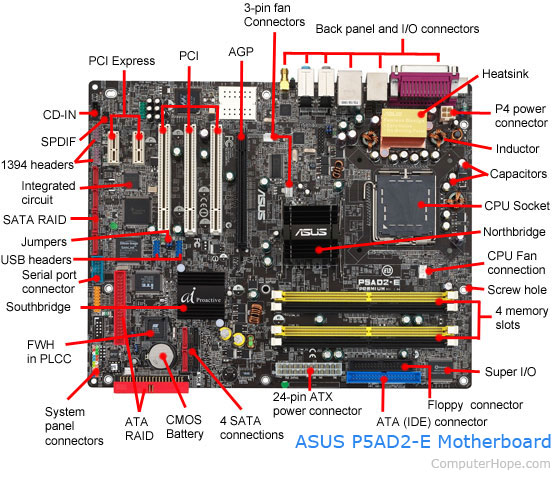
- A CPU socket – the actual CPU is directly soldered onto the socket. Since high-speed CPUs generate a lot of heat, there are heat sinks and mounting points for fans right next to the CPU socket.
- A power connector to distribute power to the CPU and other components.
- Slots for the system’s main memory, typically in the form of DRAM chips.
- A chip forms an interface between the CPU, the main memory and other components. On many types of motherboards, this is referred to as the Northbridge. This chip also contains a large heat sink.
- A second chip controls the input and output (I/O) functions. It is not connected directly to the CPU but to the Northbridge. This I/O controller is referred to as the Southbridge. The Northbridge and Southbridge combined are referred to as the chipset.
- Several connectors, which provide the physical interface between input and output devices and the motherboard. The Southbridge handles these connections.
- Slots for one or more hard drives to store files. The most common types of connections are Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) and Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA).
- A read-only memory (ROM) chip, which contains the firmware, or startup instructions for the computer system. This is also called the BIOS.
- A slot for a video or graphics card. There are a number of different types of slots, including the Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) and Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe).
- Additional slots to connect hardware in the form of Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) slots.

There are certainly a lot of acronyms to get used to! Don’t worry too much about trying to remember all the parts and their acronyms. The key is to remember that the motherboard contains the central processing unit, the memory, and all the connectors to the rest of the hardware of the computer system. The board is the ‘mother’ of all components – that’s where it gets its name.
1. AT Motherboard
These motherboards have bigger physical dimensions of hundreds of millimeters and hence they are not the right fit for the mini desktop category of computers. Bigger physical size also inhibits installing new drivers. Sockets and six-pin plugs are used as power connectors in these motherboards. These power connectors are not that easily identifiable and hence users face difficulties in connecting and using it.

2. ATX Motherboard
ATX denotes Advanced technology extended, it was developed by Intel during the 1990s and it was an improved version over an earlier version of AT motherboard. It is smaller in size when compared to AT and it provides interchangeability of the connected components. There is a marked improvement in the connector aspects.
3. LPX Motherboard
This board had two improvements over earlier versions. The first one is Input and Output ports were taken to backside and the second one was the introduction of Riser card to facilitate more slots and easier connection. Some of these features were deployed in the AT motherboard. The main disadvantage in this board is the lack of Accelerated Graphic Port (AGP) slots which led to a direct connection to PCI. Issues in these motherboards were addressed in NLX boards.
4. BTX Motherboard
BTX denotes Balanced Technology Extended, intended to manage demands of new technologies in terms of more power requirements hence generation of more heat. Intel stopped further development of BTX boards during the mid-2000s to concentrate on low power CPU.
5. Pico BTX motherboard
These boards are smaller in size and hence the word Pico. Two expansion slots are supported in spite of being sharing the top half of BTX. Half-height or riser cards are its unique features and it supports the demands of digital applications.
6. Mini ITX motherboard
It’s a miniature version of motherboard over its earlier versions. Designed in the early 2000s and its dimension is 17 x 17 cm. Mainly used in small form factor (SFF) computer due to its lower power consumption and faster cooling ability. This motherboard is the most preferred in the home theater domain due to its lower level of fan noise that will improve the quality of the theatre system.